Pixels to People: What is UI design & UX design?
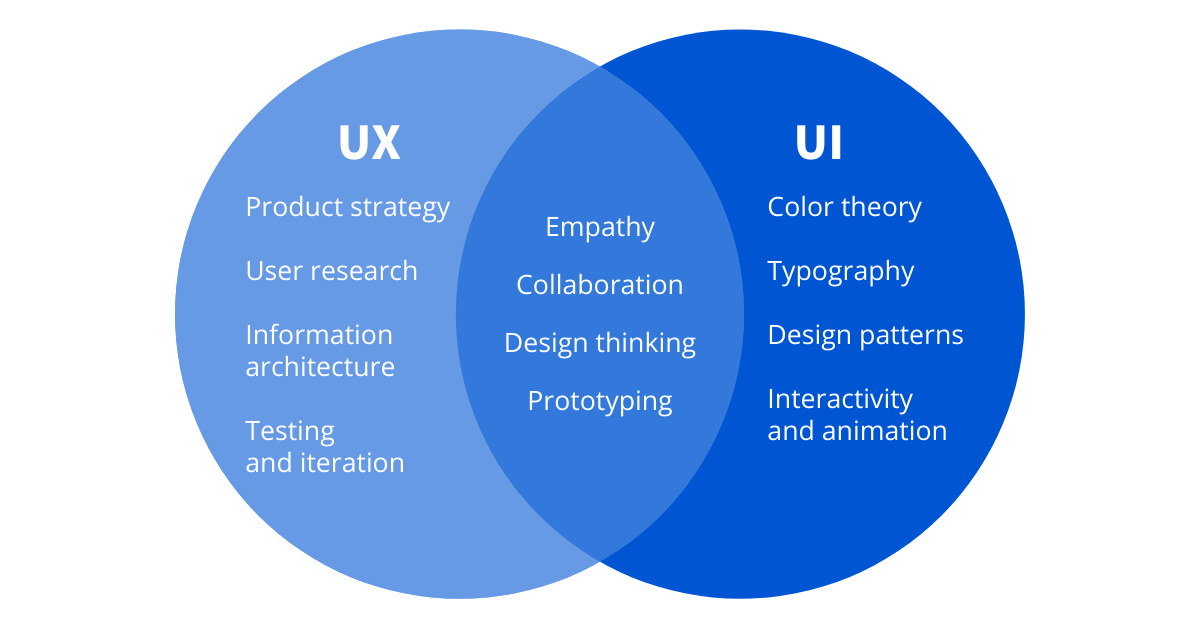
Customer experience (CX) is a broad and encompassing category that includes various aspects, with user experience (UX) being a crucial component. Within the UX process, user interface (UI) design plays a significant role in shaping the overall experience. The relationship between these elements can be illustrated in a Venn diagram, as depicted below.
UI, short for User Interface, is the graphical presentation of a digital product, such as websites and applications. Its purpose is to bridge the gap between the user and the product functionality, facilitating the desired outcome through a series of interactions between the user and the device. UI is comprised of various elements, including text, shapes, graphics, and photos, all carefully designed to create a seamless and intuitive user experience.
A well-designed UI should incorporate a range of design principles such as layout, grid structure, typography, color palettes, animations, and micro-interactions, to create an interface that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also user-friendly. UI is all that we experience — mostly with our eyes.
UX or User Experience is focused on making products easy to use by studying the interface, navigation, and communication. The aim is to make the product accessible to the largest possible user base. While the role of the UI designer is to focus on the look & feel, the UX designer’s focus is on how it works. The quality of user experience is influenced by the ease or difficulty of interacting with the interface elements crafted by UI designers.
Aside from information architecture planning, UX also covers various kinds of research (surveys, A/B tests, focus groups, interviews, workshops, and more).
CX or Customer Experience is often confused as being another name for UX. The truth is that CX is a top-level process that defines not only how your product works, but how your entire company operates.
Recently, there has been a trend among UX designers to call themselves as Product Designers. This term encompasses a broader range of skills that include UX, UI, and fundamental research, enabling them to tackle various issues.
A product designer can assist in various aspects of the development process, such as business operations, selecting the appropriate construction methodology, and designing the user interface.